Can a Bulging Disc Get Worse?
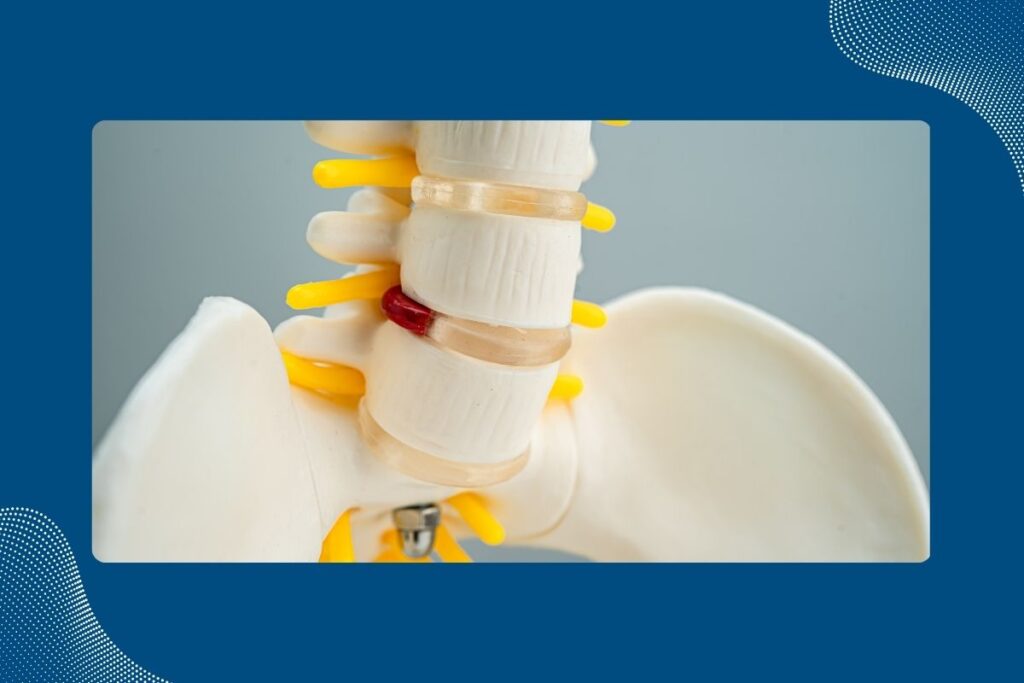
A bulging disc might not seem serious initially, but it can worsen if you don’t take care of it. In this post, we’ll talk about what happens if a bulging disc is ignored and share some key tips on how to prevent it from getting worse. You’ll learn how to manage a bulging disc through simple treatment options and changes in your daily habits. With this knowledge, you can help keep your spine healthy and avoid further problems with your bulging disc.
The Dangers of Ignoring a Bulging Disc
While initially, the symptoms of a bulging disc might be absent, the lack of treatment or preventive care can lead to the disc deteriorating further. This deterioration can get worse and lead to a herniated disc, where the inner soft center of the disc breaks through the outer part, pressing on nearby nerves and causing significant pain and disability.
Complications of an Untreated Bulging Disc
- Increased Pain and Discomfort: As the disc bulges more, it can lead to increased back pain or sciatica, characterized by sharp, shooting pains along the nerve pathways.
- Mobility Issues: As a bulging disc progresses, one might experience reduced mobility, making daily activities and tasks challenging.
- Nerve Damage: Persistent pressure on spinal nerves can lead to chronic nerve damage, resulting in numbness, tingling, or limb weakness.
- Quality of Life: The escalating symptoms can severely affect one’s quality of life, limiting work capacity, personal life, and leisure activities.
Economic & Emotional Impact
The repercussions of an untreated bulging disc extend beyond physical health, affecting emotional well-being and financial stability. Chronic pain can lead to mental health issues like depression and anxiety. Economically, it can result in lost wages due to absenteeism and increased medical expenses.
The Progression of a Bulging Disc
The anatomy of a spinal disc is designed to absorb shock and provide flexibility to the spine. However, due to factors like aging, injury, or lifestyle choices, discs can degenerate and bulge out. Understanding this progression is critical to halting or slowing the worsening of a bulging disc.
Stages of Disc Degeneration
- Disc Desiccation: The disc loses hydration and degenerates, losing its shock-absorbing capabilities.
- Disc Prolapse: The disc bulges out without rupturing the annulus fibrosus, the disc’s outer layer.
- Disc Extrusion: The nucleus material pushes out more but is still confined by the outer or spinal cord’s protective layers.
- Sequestration: The nucleus material breaks through the outer layer, becoming a free fragment in the spinal canal.
Contributing Factors
Several factors contribute to the progression of a bulging disc, including:
- Biomechanical Forces: Improper lifting, poor posture, and repetitive strain can exacerbate disc bulging.
- Aging: Natural degeneration of the disc material over time increases the risk of bulging discs.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, lack of exercise, smoking, and poor nutrition can all contribute to the worsening of a disc bulge.
Preventing a Worsening Bulging Disc
Preventive measures can significantly impact the health of your spinal discs. Here are strategies to prevent the worsening of a bulging disc:
Regular Exercise and Physical Activity
Engaging in regular, spine-friendly exercises can strengthen the muscles supporting your spine, reducing the load on your discs. Focus on core strengthening, flexibility exercises, and aerobic activities.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Proper ergonomics at the workplace and home can reduce stress on your spine. Ensure your workstation is set up to support a natural spinal posture and be mindful of your posture when lifting or performing activities.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on your spine and discs, decreasing the likelihood of a bulging disc worsening.
Signs of a Worsening Bulging Disc
Early detection of a worsening bulging disc can lead to more effective treatment and a better prognosis. Look out for these signs:
- Increased Pain: Escalating or spreading pain can indicate that the disc bulge is worsening.
- Neurological Symptoms: Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the extremities can signify nerve involvement.
- Changes in Reflexes: Altered reflexes might be observed during a neurological examination.
How to Treat a Worsening Bulging Disc
Treatment options vary based on the severity and specifics of each case. Here’s a look at the possible treatments:
Conservative Treatments
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises can improve mobility, strengthen the spine, and alleviate pain.
- Medications: NSAIDs, analgesics, and muscle relaxants can be used to manage pain and inflammation.
Advanced Interventions
- Epidural Steroid Injections: These can reduce inflammation and pain in the affected area.
- Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical options like a discectomy or laminectomy might be considered.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can have a profound impact on the health of your spine. Here are key modifications to consider:
- Diet: A nutrient-rich diet supports spinal health. Focus on anti-inflammatory foods and proper hydration.
- Stop Smoking: Smoking can exacerbate disc degeneration and impair healing.
- Activity Modification: Learn proper techniques to lift and avoid activities that strain your back.
Seeking Medical Attention
Prompt medical attention can prevent further deterioration. If you experience worsening symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan.
Key Takeaways
By thoroughly understanding each aspect of a bulging disc, from its progression and potential dangers to effective treatment strategies and lifestyle adjustments, you can take proactive steps to manage your condition and enhance your quality of life. Maintaining an informed dialogue with healthcare providers, staying vigilant for symptoms, and adopting a spine-healthy lifestyle are essential to managing a bulging disc.